
To try to understand how harmful algal blooms might evolve in Lake Erie in a warming climate, University of Michigan scientists helped conduct a survey of cyanobacteria in a gulf of Kenya’s Lake Victoria.

For many, resilience work begins at home. University of Michigan experts are taking a local lens to the climate crisis and other broad sustainability challenges, examining opportunities in infrastructure, community planning, mobility, and public policy across the State of Michigan. The Center for Local, State and Urban Policy, the Great Lakes Integrated Sciences and Assessments Program, and other partnerships work to enable sustainable solutions for the U-M community, the state, and the Great Lakes region.

To try to understand how harmful algal blooms might evolve in Lake Erie in a warming climate, University of Michigan scientists helped conduct a survey of cyanobacteria in a gulf of Kenya’s Lake Victoria.

At the core of Campus Plan 2050 is a commitment to sustainability. The initiative proposes innovative infrastructure solutions, including geo-exchange systems designed for efficient heating and cooling through ground-source heat pumps, as well as extensive building retrofits that enhance energy efficiency and sustainability, and efficiency upgrades to the transit system.

Along M-22 in northwestern Michigan, people with mobility challenges can access breathtaking views of Lake Michigan from a 300-foot-high platform, explore rare birds and plants in a restored marsh or lose themselves in coastal dunes and forests once off-limits.
The pathway to improving the health of hundreds of thousands of residents in Michigan’s largest cities is laid out in a new information hub that provides a panoramic look at the major factors impacting the wellbeing of these individuals.

In collaboration with the Michigan Climate Action Network (MiCAN) and Michigan Environmental Justice Coalition (MEJC), a group of 20 selected U-M graduate students recently published a comprehensive report about Michigan’s public power options.
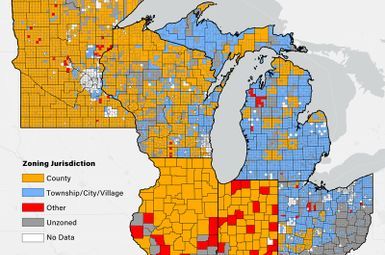
The Center for EmPowering Communities, with funding from the U.S. Department of Energy Solar Energy Technologies Office and the Michigan Department for Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy, has expanded its pioneering renewable energy zoning database to detail solar zoning regulations across the Great Lakes region.

The percentage of Michigan local governments that say they have or are considering renewable energy goals has doubled since 2019. Local officials also report that a variety of energy issues, such as energy infrastructure zoning and planning for electric vehicles, are more relevant to their communities than they were four years ago, and the tone of local policy discussions regarding zoning for renewable energy infrastructure is generally seen as constructive.

A grant from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Integrated Ocean Observing System will establish a Great Lakes Biodiversity Observation Network to coordinate with and learn from biodiversity observation networks along the U.S. coasts and ocean waters and other BONs in ocean and freshwater habitats worldwide.

Currently the director of the Office of Energy Justice and Equity and the secretarial adviser on equity at the U.S. Department of Energy, and formerly the department’s chief diversity officer, Baker will advance sustainability education and research across U-M schools and colleges.

Great Lakes researchers at U-M have been awarded a $6.5 million, five-year federal grant to host a center for the study of links between climate change, harmful algal blooms and human health. Increased precipitation, more powerful storms and warming Great Lakes waters all encourage the proliferation of harmful algal blooms composed of cyanobacteria.
The U.S. National Science Foundation has awarded a three-year, $614,000 grant to U-M and its international partners to create a new research initiative that will address the socioeconomic vulnerabilities of climate migrants in the Lake Victoria Basin (LVB) and Great Lakes Region (GLR).

Converting home heating systems from natural gas furnaces to electric heat pumps is seen as a way to address climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. But a new U-M study of 51 Southeast Michigan households shows that switching to efficient, cold-climate heat pumps would increase annual utility bills by an average of about $1,100.

Three new U-M sustainability catalyst grants will support novel research projects to address vexing environmental challenges. “Catching the Waves” focuses on deploying wave energy converters to power remote coastal communities, starting with Beaver Island in Lake Michigan. “Mussel Roads” uses biomimicry to enhance asphalt durability by developing materials inspired by mussel-binding proteins. “Plast-ick,” leverages artificial intelligence and satellite data to predict pollutants like PFAS in water bodies.

According to a U-M survey, 86% of respondents either strongly or somewhat support adding rooftop solar panels. The survey found some regional variation: Rooftop solar drew support from 83% of leaders in the Upper Peninsula, while garnering 89% support from southeastern Michigan officials.
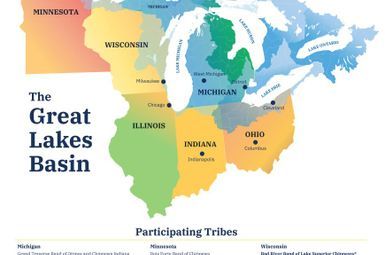
“Given that we sit in the heart of the Great Lakes and 21% of the world’s fresh surface water, we wanted to explore the region’s plans to identify the highest-impact, most innovative and scalable multi-state opportunities. We looked for what was working, to inform ways to accelerate community-based climate action."

The new projects include “Plast-ick,” which leverages AI and satellite data to predict pollutants like PFAS in water bodies; “Catching the Waves,” which focuses on deploying wave energy converters to power remote coastal communities; and "Mussel Roads," which uses biomimicry to enhance asphalt durability by developing materials inspired by mussel-binding proteins.

The U-M Biological Station, a more than 10,000-acre research and teaching campus along Douglas Lake just south of the Mackinac Bridge, will host distinguished scientists, artists and authors from across the United States as part of its 2024 Summer Lecture Series.

Local officials across Michigan increasingly view electric vehicle infrastructure planning as relevant for their governments, though many cite too few public charging stations and costs associated with adding them as barriers to expansion.

Researchers at U-M’s Rogel Cancer Center want to build a movement to understand how exposures to toxic metals, industrial pollution and “forever chemicals” called PFAS, are impacting the health and cancer risk of residents across Michigan.
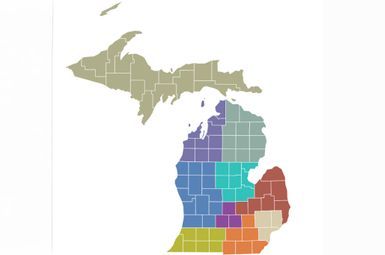
A new data map showcasing diverse indicators of poverty and well-being throughout Michigan highlights the key challenges confronting residents in different parts of the state and suggests interventions for the state’s most critical needs.

U-M is marking late March and all of April with a series of events focused on sustainability and climate action, continuing a tradition that began with the first “Teach-In on the Environment” in 1970—which grew into what is now known as Earth Day.

Improving the U.S. electricity grid is necessary to lower costs, boost reliability and help tackle climate change, but it will take some serious soul searching by the leaders of entities that control the grid.

The ClimateCAP MBA Summit, a conference that aims to prepare future business leaders on how to understand and respond to the climate crisis, was hosted at U-M this year.

Rackham Ph.D. candidate Etienne Herrick-Sutton works with Great Lakes region farmers to identify strategies for improving the environmental and economic outcomes of cover cropping.

The threat of harmful algal blooms (HABs) continues to plague Lake Erie, prompting intensified efforts from binational jurisdictions to address this persistent environmental challenge. Central to this endeavor is the mitigation of phosphorus, recognized as a key driver of algal blooms, through coordinated action plans.

The City of Ann Arbor recently reached out to the Center for Sustainable Systems (CSS) to design a model of a geothermal energy system. The model will be used for public education and community outreach in Ann Arbor.

This winter, researchers at the U-M Biological Station in northern Michigan are strengthening their snow science with new technology to track the snowpack at an hourly rate and get a deeper understanding of the complexities of global environmental change.

Four newly awarded sustainability “catalyst grants” at U-M are piloting innovative ways to bolster climate resilience and sustainability. Funded by the U-M Graham Sustainability Institute, these projects will explore renewable energy deployment in Nepal, climate justice in the Midwest, textile recycling innovation and equitable transportation planning.

The need for a compact came when, twenty-five years ago, a Canadian company decided they could fill tanker ships with Great Lakes water to sell to countries with water shortages. Wanting to protect the lakes, the Great Lakes states, along with Ontario and Quebec, began the complex negotiations that would lead to the formal agreement detailing how they’d work together to manage as well as protect the Great Lakes.

The Environmental Health Research-to-Action Academy is a community-academic partnership focused on building skills and intergenerational knowledge in environmental health, community science and policy advocacy to address cumulative environmental exposures in the nearby communities.

Associate Professor Tony Reames will be returning to the University of Michigan School for Environment and Sustainability (SEAS) from his leave of absence at the Department of Energy (DOE), where he served as the Principal Deputy Director for State and Community Energy Programs and the DOE’s Deputy Director for Energy Justice. Reames will become the Tishman Professor of Environmental Justice at SEAS and serve as the new Director of the SEAS Detroit Sustainability Clinic, effective January 2024.

Flint residents have learned to question everything in the decade since the city’s drinking water first began showing signs of lead contamination. Even now, after seven straight years with water meeting federal safety guidelines, the lack of trust remains for many. U-M researchers and their partners are addressing this lingering problem on multiple fronts — from continued testing to in-school education and consulting with the city.

As part of the Great Lakes St. Lawrence Governors and Premiers’ new initiative aimed at planting 250 million trees in the Great Lakes region by 2033, the U-M School for Environment and Sustainability partnered with the Michigan Department of Natural Resources ( and GSGP to hold a ceremonial tree planting on November 9 at one of SEAS’ research natural areas.

A U-M Public Health research team will support community leaders from the Southwest Detroit Community Benefits Coalition and the Southwest Detroit Environmental Vision, who are working to develop an app that quantifies truck traffic using data from phones and other electronic devices.

More than 100 U-M community members gathered Nov. 3 at the site of the future Central Campus residential development to observe construction efforts that will advance the university’s progress toward carbon neutrality.

LSA’s Detroit River Story Lab teaches students from elementary school through college about the past and future of the vibrant body of water.

Ann Arbor and other cities across the Midwest and Northeast have been referred to by climate specialists as “climate havens,” natural areas of refuge that are relatively safe from extreme weather events such as intense heat and tropical storms.

“Over a third of the energy we use in our homes goes to waste. That’s a lot! Programs like TCLP’s are essential in helping residents save money, support their health, and protect the environment.”

Nearly $1.23 billion has been spent by the U.S. government since 2004 on the cleanup of toxic pollutants in waterways resulting from manufacturing activities in historic areas around the Great Lakes.

“Water management will be one of the challenges of our generation,” Gilchrist told students. “In order to understand how we can meet that challenge, we need smart, we need bold, we need connected information professionals to be part of the process.”

Since 2010, the university has reduced its total greenhouse gas emissions by 28%, even as total building area has increased by 14%. U-M is on pace to reduce its total quantified emissions by 50% by 2025, exceeding Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change guidance to reduce emissions by 45% by 2030.

We are in an “extraordinary moment” to create an equitable clean energy future. And Michigan, like other states, is an “essential part” of bringing forth that future.

"Michigan’s legislative leadership earlier this year announced its intention to introduce a package of bills to accelerate the Mi Healthy Climate Plan. Recently, Governor Whitmer put her support behind the proposal and echoed what those involved in the renewable energy transition have noted for some time: the current approach to permitting clean energy projects is broken."
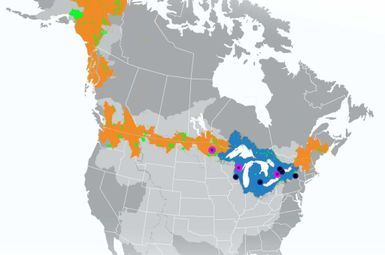
U-M researchers will lead a new effort to strengthen the climate change resilience of vulnerable communities that span international boundaries and jurisdictions. The U.S. National Science Foundation has awarded $5 million to U-M to establish the Global Center for Understanding Climate Change Impacts on Transboundary Waters.

“Water conservation and access” brings a slew of images to mind: wastewater flowing through main lines to a city treatment plant, a fisherman yanking invasive mussels off the hull of a trawler, the installation of filters in communities that lack access to safely managed drinking water.